PandaSuite Database
The PandaSuite Database is not a traditional database. It’s a data model you create in PandaSuite Studio, which gets copied to each device. Each user owns their own local version that they can modify without impacting others.
How does it really work?
Think of the PandaSuite Database as a starter template for your data:
- In PandaSuite Studio: you design a schema (structure) with default values.
- On download: each user receives a personal copy of this template.
- During use: changes remain local to each device.
Traditional database: all users share the same data on a server.
PandaSuite Database: each user has their own copy that they can modify independently.
Key takeaways
- Each device = an independent copy: user changes do not affect others.
- Persistent data: it survives app closure (but not uninstallation).
- Optional synchronization: you can fetch model updates from PandaSuite Studio.
- No server required: everything works locally, even offline.
Two main use cases
User’s local storage
To save information specific to each user:
- Scores & progress: game level reached,
- Preferences: chosen language, dark mode enabled,
- App state: tutorial completed, pre-filled forms.
Content that drives your app
To create dynamic content from PandaSuite Studio:
- Product catalog: regularly updated list of items,
- Dynamic pages: editorial content without rebuilding the app,
- Configuration: app settings editable remotely.
In this second case, you can update the content in PandaSuite Studio, and users fetch these changes via the Fetch remote data action.
Create your database
Add the database
In the Database panel, choose PandaSuite Database.
The component is added at the Project level so it’s accessible everywhere.
Click the arrow to open your database.
Define the structure
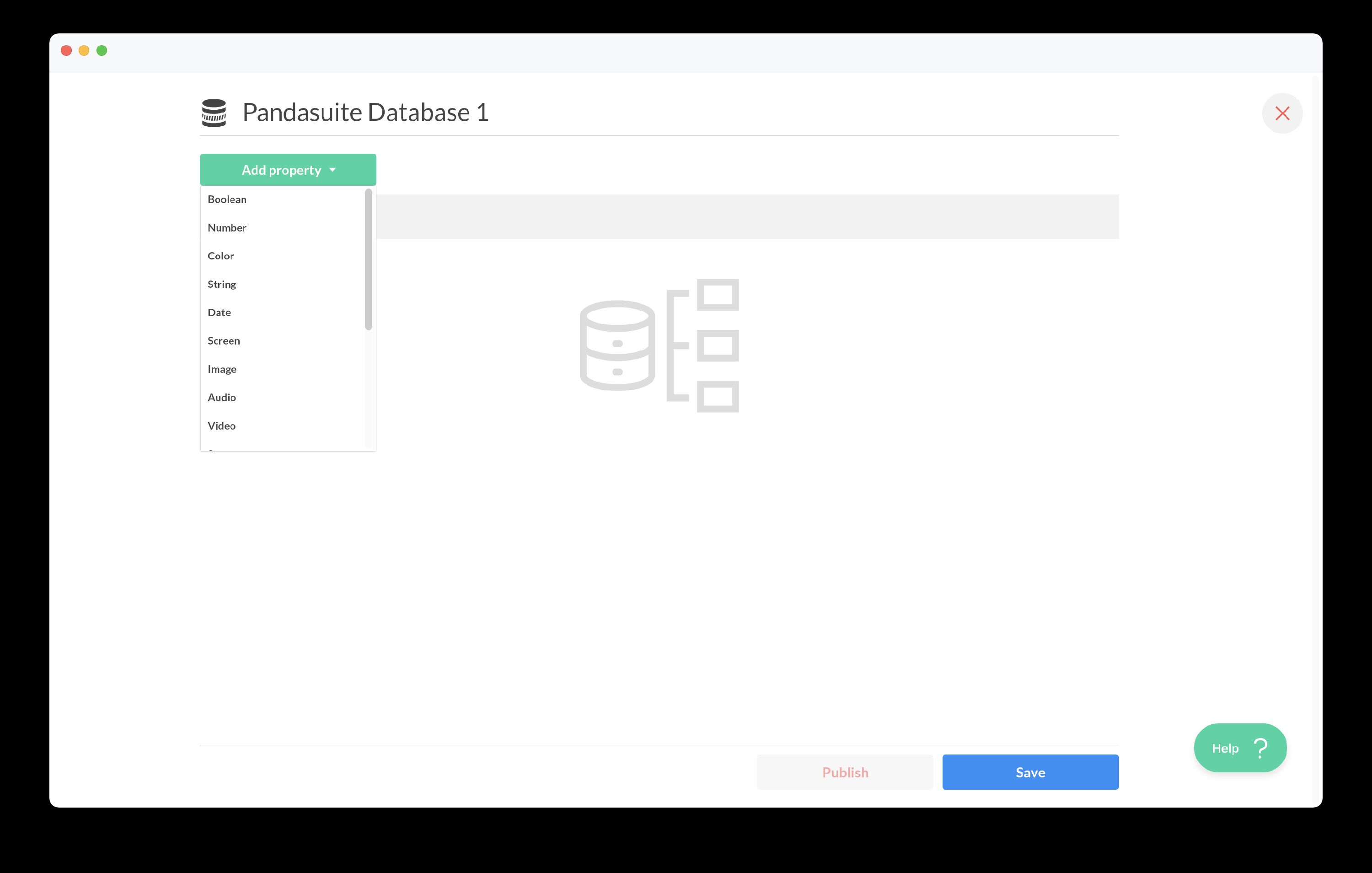
- Click the + Add property button
- Choose the data type (Text, Number, Array, Image…)
- Rename and set the default value if needed.
Each change requires you to Save and Deploy to include it in your builds or remote preview.
Manipulate data
All operations are triggered from the Actions panel — no code required.
Create / Edit data (local)
This action edits data only on the user’s device.
It’s the most common action for handling scores, preferences, or app state.
These edits stay on the device. They’re not sent to PandaSuite servers or shared with other users.
-
Trigger
Select any trigger — e.g., On Tap of a “Validate” button. -
Action
Interact with a data source → PandaSuite Database → Create/Edit data (local) -
Target
Pick the property to modify in your database. -
Function to apply
For simple values (text, number…)
-
Set: fully replaces the value
Example: change the player’s name -
Increment/Decrement: adds or subtracts a number
Example: increase the score by 10 points⚠️ Works only on
Numberdata types.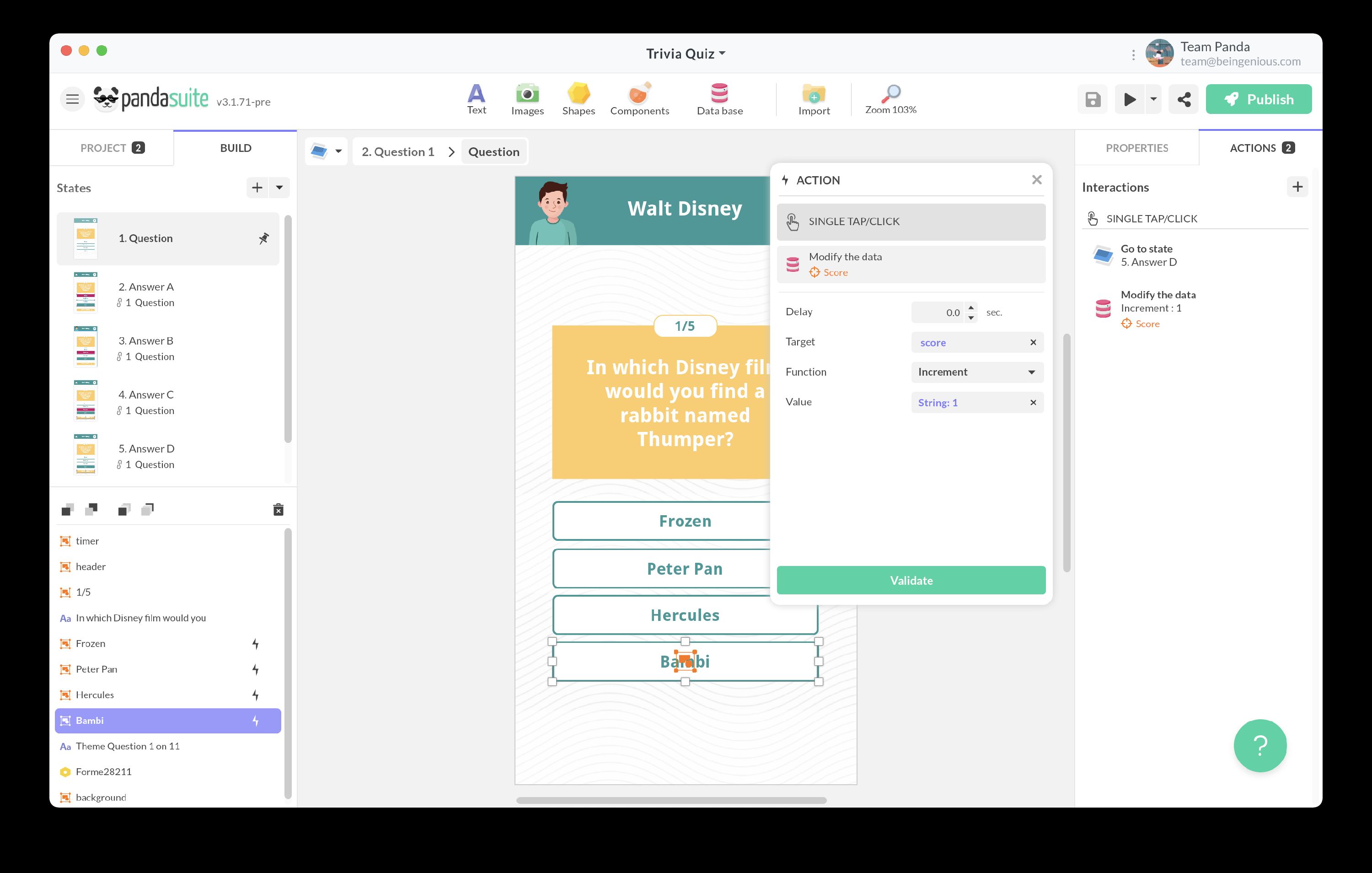
For arrays (lists):
-
Add: appends an item to the list
Example: add a product to the cart -
Remove by value: removes a specific item
Example: remove “Apple” from the shopping list -
Remove by id: removes an item by its unique ID
Example: remove product #42 from the cart
For any data type:
Delete: completely deletes the data
Example: reset user preferences
- Value
Define what you want to store:
- Fixed text: Hello
- Dynamic value: bind to a form field
- Function:
timestampfor current date,randomfor a random number
Fetch remote data
This action retrieves updates to the model from Studio — especially useful for dynamic content.
How does synchronization work?
You have two options:
-
Overwrite all: completely replaces local data with data from PandaSuite Studio
- ✅ Ideal for: product catalog, editorial content
- ❌ Beware: overwrites local changes (scores, preferences)
-
Merge: intelligently combines local and remote data
- ✅ Keeps: user changes
- ✅ Adds: new items from Studio
- ✅ Updates: default values not modified locally
You have a collection of game levels. The user unlocked levels 1 to 5.
You add 3 new levels in Studio.
Without merge: the user loses their progress.
With merge: the user keeps their progress and gets the new levels.
When to sync?
| Moment | Why |
|---|---|
| On app launch | Retrieve the latest updates |
| “Refresh” button | Let the user trigger it manually |
| After regaining internet | If the app was used offline |
Export data (local)
This action creates a CSV file containing all the user’s local data. Useful for:
- Analytics: understand how users interact with the app
- Support: troubleshoot issues
- Backup: let the user save their progress
The CSV is created and stored on the device. To send it to a server, you’ll need to use an external API.
Delete your database
Go to the Project tab and select your database.
Click the delete icon.
Understand the limits (and how to work around them)
What the PandaSuite Database does NOT do
-
No automatic sync between users
- ✅ Solution: use Firebase or an API to share data.
-
No complex queries (like SQL)
- ✅ Solution: keep data simple and use component filters.
-
No automatic cloud backup
- ✅ Solution: offer a CSV export or connect to a cloud service.
Its strengths
- Simplicity: no server management required
- Performance: local data = instant access
- Offline-friendly: works without internet
- Free: included in PandaSuite
The PandaSuite Database is perfect for 90% of apps. For the other 10% (multiplayer apps, sensitive data…), combine it with external services.